How Does an Oxygen Generator Work for Industrial Use?
In modern industrial manufacturing, there is a widespread demand for high purity oxygen across different applications. Sourcing the required quantities of oxygen gas can be made cost-effective with access to a dedicated oxygen generator.
This article describes how an industrial oxygen generator works and outlines the most common applications for the generated gas.
What Is an Oxygen Generator?
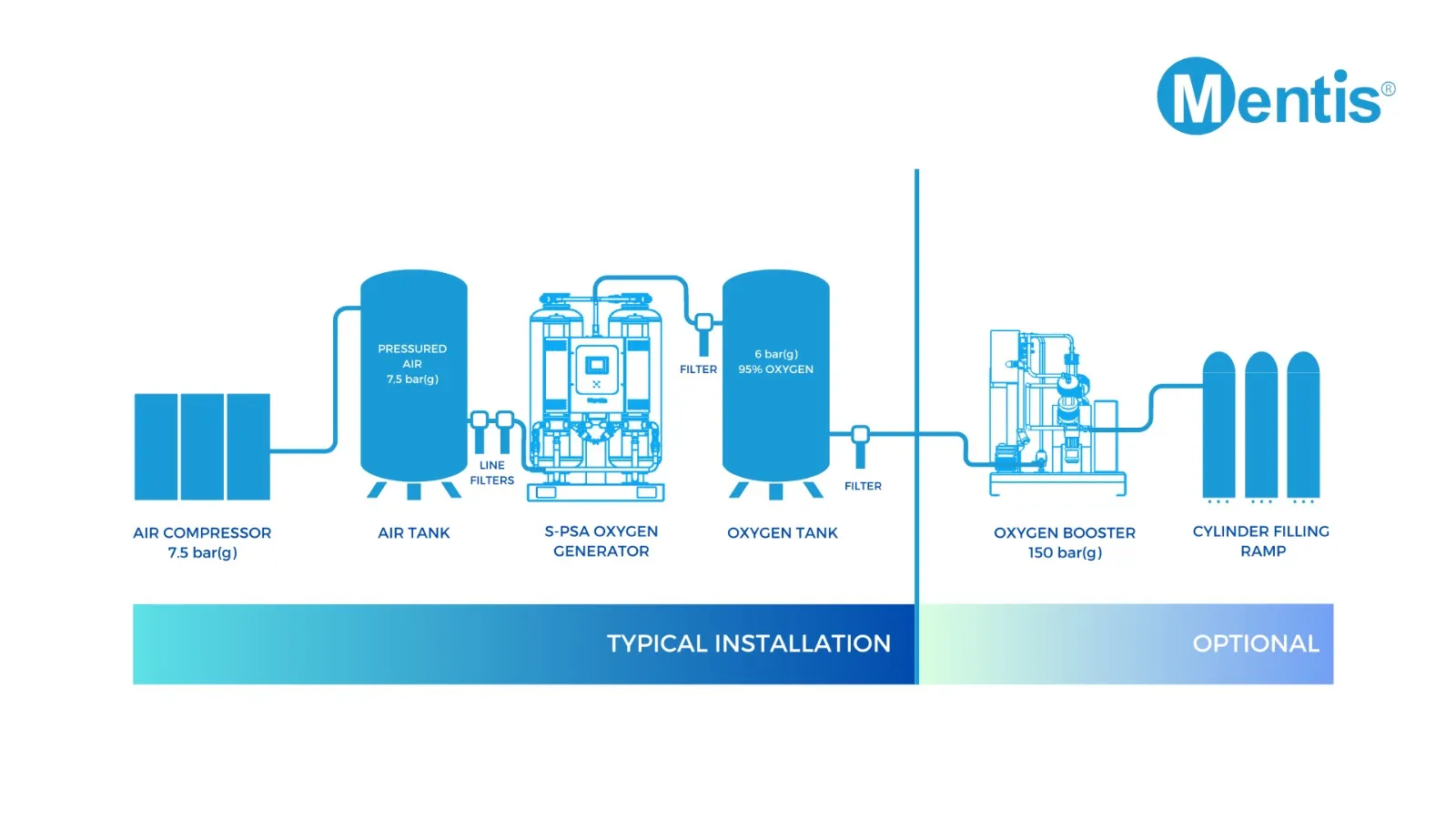
An oxygen generator is a device that separates oxygen from compressed air using special selective adsorptive technology called pressure swing adsorption (PSA). The compressed air used in the oxygen generation process has a similar composition to ambient environmental air with 21% oxygen and 78% nitrogen. The oxygen contained in the compressed air is allowed to flow through a zeolite molecular sieve which retains nitrogen resulting in high purity oxygen at gas production outlets.
Operating Principles for a PSA Oxygen Generator
The pressure swing adsorption process for a PSA oxygen generator is essentially the same as that of a nitrogen generator with one major distinction.
The adsorptive material inside its molecular sieve is made of zeolite rather than carbon found in a nitrogen PSA device.
During a routine operation, compressed air channeled through the oxygen generator will be separated into its component gases.
The zeolite molecular sieve will selectively adsorb nitrogen that meets it while allowing high purity oxygen gas to flow onwards to a product gas outlet.
A unique feature of zeolite that makes it ideal for an oxygen generator is its ability to released retained nitrogen gas once the pressure within the generator is eased.
This makes it quite easy to regenerate the medium for a further cycle of oxygen generation.
Oxygen Generator Applications
Oxygen generators are currently in use in a broad range of commercial and industrial manufacturing applications. These devices play a crucial role in providing useful quantities of oxygen gas required to drive various processes.
Typical applications for PSA oxygen generators include:
Sewage and wastewater treatment plants
Glass manufacturing
Food/Beverage industries
Papermaking
Metallurgy
Chemical oxidation processes
Commercial fish farming
Mining
Gasification processes
How Does an Oxygen Generator Work?
An oxygen generator using PSA technology utilizes the ability of adsorbent zeolite material to separate a stream of compressed air into its component gases.
The pressure swing adsorption process to produce high purity oxygen is a two-stage cycle that involves simultaneous adsorption and desorption activities in two generation towers.
Adsorption
The adsorption stage of oxygen generation uses an adsorptive tower packed with molecular zeolite pellets that selectively retains nitrogen while allowing oxygen to pass into a collecting tank as product gas under pressure.
This process of selective adsorption will continue until the adsorptive tower reaches its maximum saturation point at which the zeolite sieve can no longer absorb more nitrogen gas.
Desorption
This second step in the PSA oxygen generation process is essentially a reversal of the adsorption process. Once the saturation point for a tower in the adsorptive phase is reached, its function is altered. Regeneration of the zeolite material is by rapidly depressurizing the cylinder to release absorbed nitrogen gas into the atmosphere.
The entire PSA process is automated with a central regulatory unit detecting oxygen and nitrogen gas saturation levels in both the adsorption and desorption towers. The phase switch is done by opening or closing the appropriate process valves and raising or reducing the pressure within the zeolite packed cylinders.